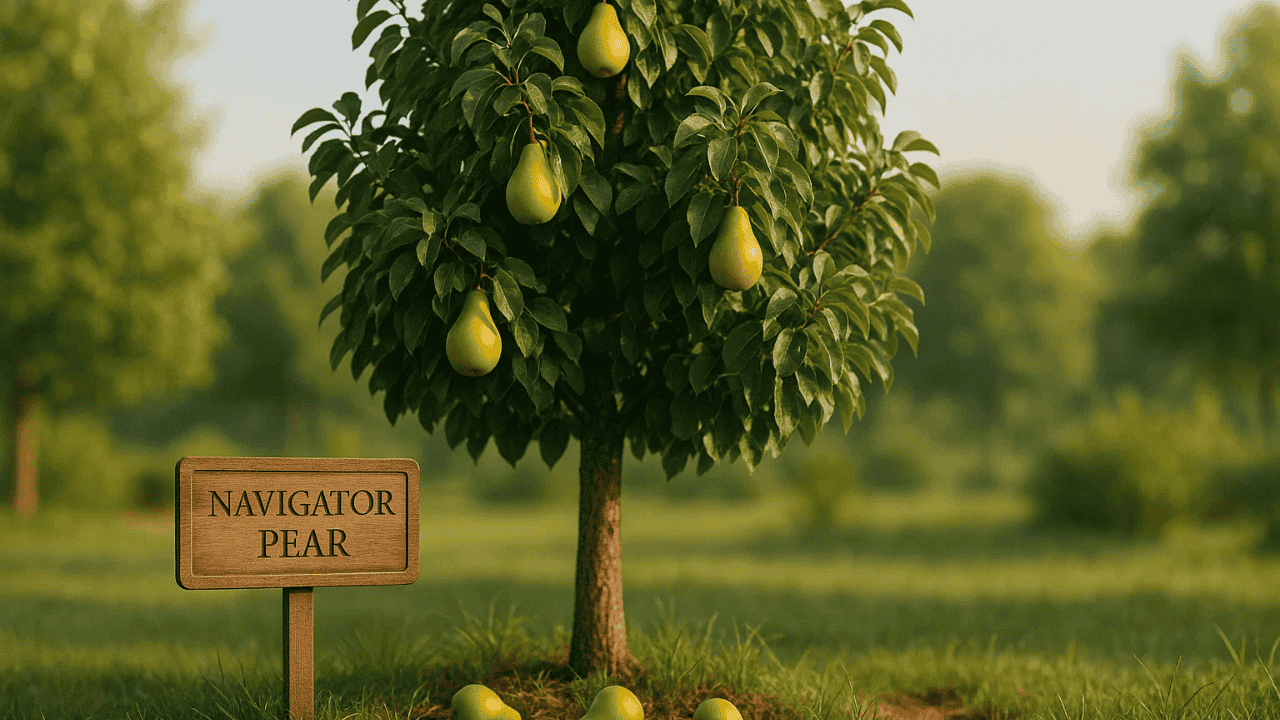
When people search for a tree that provides beauty, shade, and the potential for delicious fruit, the navigator pear often becomes an attractive option. The navigator pear offers a blend of ornamental value and practical usefulness, making it suitable for home gardens, landscaped areas, pathways, and even compact outdoor spaces. This guide covers everything from characteristics and planting requirements to its long-term appeal for gardeners and homeowners.
The navigator pear stands out because it offers far more than seasonal flowers. It grows in a neat, upright shape, develops vivid foliage, and may produce fruit under the right conditions. That makes it an ideal candidate for anyone interested in a tree that delivers results without consuming too much space or requiring complicated care.
What is navigator pear
Navigator pear is a pear cultivar developed to offer resilience, manageable size, and appealing structure. It is recognized for its upright form, balanced branch pattern, and visually pleasing foliage. While some pear varieties are grown strictly for fruit, navigator pear is appreciated for both its landscaping appeal and the possibility of homegrown pears.
Many gardeners choose navigator pear because they want something that looks good all year. In spring, flowers appear before the tree fully leafs out. In summer, it produces dense green foliage. In autumn, its leaves shift into golden and warm tones, providing an eye-catching display. These features make navigator pear suitable for a variety of outdoor settings.
Growth habit and seasonal appearance
Navigator pear typically reaches a medium height that ranges around 23 to 30 feet when fully mature. The trunk and branches establish a symmetrical, upright form, which makes the tree appear clean and sculpted. Unlike trees that sprawl widely, navigator pear keeps a narrower width, so it can be planted close to walkways, fences, property lines, or patios.
During early spring, navigator pear develops clusters of white blossoms. These blossoms appear before most leaves, which makes the tree stand out when other plants are just awakening from winter. Once the flowers fade, fresh green foliage emerges. Through summer, the tree provides shade and structure. The fall transformation is another highlight, as the leaves shift into warm yellow, amber, or orange shades.
Because of these seasonal changes, navigator pear contributes year-round value, rather than serving as a single-season attraction.
Soil and climate requirements
Navigator pear thrives best in well-drained soil. Heavy, overly compacted soil can restrict growth if not amended. Adding compost during planting improves root development and overall vitality. The tree prefers a location that receives full sunlight. At least six hours of consistent light helps ensure steady growth, flowering, and fruit-forming potential.
Navigator pear adapts well to various climates. This adaptability is one reason it is widely used in regions with noticeable seasonal changes. Cold tolerance, wind resistance, and a dependable growth rate make navigator pear practical even in environments where other trees struggle.
How to plant and establish navigator pear
When planting navigator pear, preparation plays an important role. Select a site with full sun and adequate spacing away from structures so the tree can grow naturally. The planting hole should be wider than the root ball but not deeper. Position the tree so the root flare remains level with the ground surface.
Water deeply after planting and maintain moisture during the first growing season. Applying mulch around the base helps retain soil moisture and regulate temperature. However, mulch should not touch the bark directly because this can lead to decay.
Once established, navigator pear requires less frequent watering. Its root system develops well when soil drains effectively, and this makes it more self-sufficient over time.
Long-term care for navigator pear
Navigator pear will remain structurally strong with a minimal amount of pruning. The recommended time to prune is during late winter or early spring before significant growth begins. Remove any crossing branches or damaged limbs, and shape the tree so that light and air reach central areas.
Fertilizing lightly during early growth phases supports healthy development, though excessive feeding is unnecessary. As the tree matures, navigator pear typically maintains its form naturally, needing only occasional shaping.
Regular observation is useful. If the tree receives enough sunlight and water during its early years, it usually grows into a sturdy, low-maintenance landscape feature.
Fruit development and potential uses
Some variations of navigator pear produce fruit suitable for eating. These pears often have a crisp, juicy interior and a balanced sweetness that works well for fresh consumption. When harvested at the right stage, the fruit maintains firmness, does not bruise easily, and retains texture when sliced.
Navigator pear fruit can be used in several ways:
• Eating fresh after ripening
• Slicing for charcuterie or cheese platters
• Poaching for desserts
• Using in fruit sauces or preserves
While fruiting is not guaranteed every season, proper care increases the likelihood. Pollination improvements, consistent sun exposure, and stable watering habits contribute to better yields.
Landscape applications of navigator pear
Because of its refined shape and moderate size, navigator pear is often incorporated into landscaped areas as a focal tree. Placed near entryways or lined along driveways, multiple navigator pear plantings create structure and symmetry. It works well for residential landscapes, commercial spaces, public paths, small urban gardens, school yards, and courtyards.
Some reasons landscapers specifically select navigator pear include:
• Better height control compared to aggressive shade trees
• Elegant blooming characteristics
• Seasonal foliage color changes
• Space-efficient canopy
Navigator pear also tends not to overwhelm nearby plantings, which allows shrubs, groundcovers, or flowering beds to thrive beneath and around it.
Benefits of choosing navigator pear
Navigator pear has become popular for several reasons:
• It provides attractive flowers and foliage for at least three major seasons
• It thrives in climate ranges unsuitable for more delicate trees
• It retains shape without needing constant trimming
• It may provide edible fruit
• It grows in compact areas without spreading too wide
Gardeners appreciate that navigator pear brings immediate aesthetic benefit, while mature trees continue delivering structure and shade.
Limitations or considerations
Navigator pear, like any tree, comes with expectations to manage. Some forms may produce limited fruit or may not fruit every year. Establishment years are highly important, so watering and proper soil conditions must be maintained in early growth stages. Lack of pruning can cause crowded branching, though this is easily corrected during seasonal trimming.
For anyone expecting large commercial-grade yields, navigator pear may not be ideal. For homeowners wanting moderate yield and appealing landscape value, navigator pear becomes a good match.
Conclusion
Navigator pear provides visual charm, manageable height, and adaptability, making it ideal for both decorative and informal home orchard use. Its steady upright shape, appealing bloom cycle, and ability to brighten autumn landscapes give it an advantage over many other ornamental trees. When maintained properly, navigator pear can reward owners with fruit, shade, and dependable seasonal interest. That balance of beauty and function is what allows navigator pear to remain a credible choice for homeowners planning gardens that feel inviting and organized.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Does the navigator pear tree need much pruning?
Navigator pear only needs light pruning to remove damaged, crossing, or crowded branches and to keep airflow healthy.
2. Can navigator pear produce edible fruit?
Yes, navigator pear may develop edible fruit with sweet and firm flesh, especially when given adequate care and sunlight.
3. Is navigator pear suitable for small gardens?
Navigator pear grows upright rather than wide, so it fits smaller areas more comfortably than wider-spreading trees.
4. How much sunlight does navigator pear need?
Navigator pear requires at least six hours of full sunlight each day for best flowering, shaping, and fruit potential.
5. How tall does navigator pear grow?
Navigator pear tends to reach medium height, usually within the approximate range of 23 to 30 feet when fully mature.